[ad_1]
Fast Take
An evaluation of the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX), a vital market indicator typically used to measure the market’s expectation of future volatility, reveals intriguing patterns. The analysis of common each day change within the VIX from 1990 to 2023 signifies a propensity for the index to dip markedly on Fridays, with Tuesdays trailing. This pattern substantiates the present concept of VIX compression on Fridays, including empirical validation to this widespread market perception.
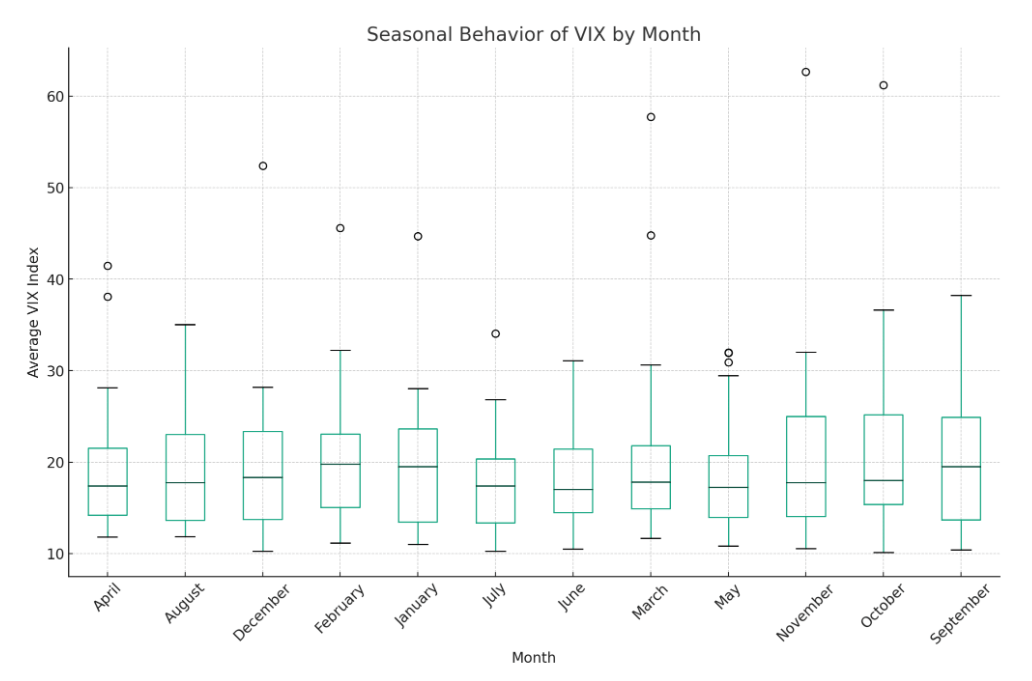
On a broader scale, a boxplot distribution of the typical VIX index throughout every month of those years unveils seasonal tendencies. October and November, characterised by wider VIX distributions, are indicative of heightened variability. This remark reinforces the notion of those months being extra liable to volatility. On the flip aspect, months reminiscent of Might and June exhibit decrease VIX averages, signaling durations of diminished volatility.
Apparently, sure months like October highlight outliers, suggesting cases when the VIX notably deviated from its typical vary. This signifies years when volatility within the equities market reached distinctive highs or dipped to uncommon lows.
These insights into the weekly and seasonal VIX patterns present a data-driven lens to grasp the rhythm of the equities market, a vital side of strategic monetary planning and decision-making.

The submit Surges in market volatility pinned to autumn months appeared first on CryptoSlate.
[ad_2]
Source link



